Article contents
Design of multi-layered TiO2–Fe2O3 photoanodes for photoelectrochemical water splitting: patterning effects on photocurrent density
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 November 2016
Abstract
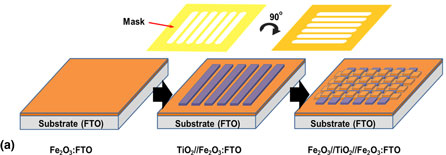
We report the effect of patterning on photoelectrochemical (PEC) water-splitting performance. Oxide–oxide heterostructures based on horizontal and vertical heterojunctions were fabricated on transparent conductive oxide glass by sequential plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) of individual metal oxide. Featured masks were employed to enable three-dimensional patternings of stripes and cross-bars structures formed by Fe2O3 and TiO2 layers. PEC measurement was carried out by a three-electrode cell. It was found that double layered TiO2//Fe2O3:FTO showed a decrease in PEC performance when compared with single Fe2O3:FTO layer, whereas triple-layered Fe2O3//TiO2//Fe2O3:FTO (both patterned and unpatterned samples) displayed enhanced photocurrent density. The results show that the existence of multiple phase boundaries does not always add up to PEC enhancement observed in single heterojunction.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
- 8
- Cited by





